前文介绍了多项式回归的方式,来提升非线性数据在线性回归模型上的表现,本文介绍另一种重要方法,对数据进行分箱,也就是离散化。与线性回归相比,我们常用的一种回归是决策树回归,但决策树回归非常容易过拟合,而分箱就是非常好的一种防止过拟合,提高模型泛化能力的方法。
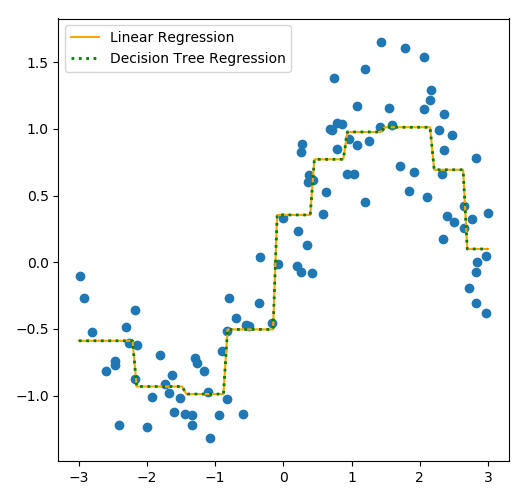
下面我们依然用多项式拓展例子中的sin曲线数据,来先做分箱操作,在对数据进行线性回归和决策树回归拟合。
代码示例
1、生成数据集
import numpy as np rnd = np.random.RandomState(24) x_rnd = rnd.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) y = np.sin(x_rnd) + rnd.normal(size=len(x_rnd)) / 3 x = x_rnd.reshape(-1, 1)
2、线性回归和决策树回归
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor as DTG from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression as LR line = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100).reshape(-1, 1) # 线性回归 lr = LR() lr.fit(x, y) y_lr = lr.predict(line) # 决策树回归 dtg = DTG() dtg.fit(x, y) y_dtg = dtg.predict(line)
3、分箱
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer # 分10箱,用onehot编码 enc = KBinsDiscretizer(10, encode='onehot') x_bins = enc.fit_transform(x, y) # 测试集分箱 line_bins = enc.transform(line) # 线性回归 lr_ = LR() lr_.fit(x_bins, y) y_lr_ = lr_.predict(line_bins) #决策树回归 dtg_ = DTG() dtg_.fit(x_bins, y) y_dtg_ = dtg_.predict(line_bins)
4、画图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt fig, (ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 5), sharey='row') ax1.scatter(x_rnd, y) ax1.plot(line, y_lr, c='orange', label='Linear Regression') ax1.plot(line, y_dtg, c='green', label='Decision Tree Regression') ax1.legend() ax2.scatter(x_rnd, y) ax2.plot(line, y_lr_, c='orange', label='Linear Regression') ax2.plot(line, y_dtg_, c='green', linestyle=':', linewidth=2, label='Decision Tree Regression') ax2.legend() plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
由对比图可以看出,分箱后不管是线性回归,还是决策树回归,都非常好的拟合了sin曲线,还消除了过拟合的问题。
本文为 陈华 原创,欢迎转载,但请注明出处:http://ichenhua.cn/read/297
- 上一篇:
- 动态规划之钢条切割问题



