给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例
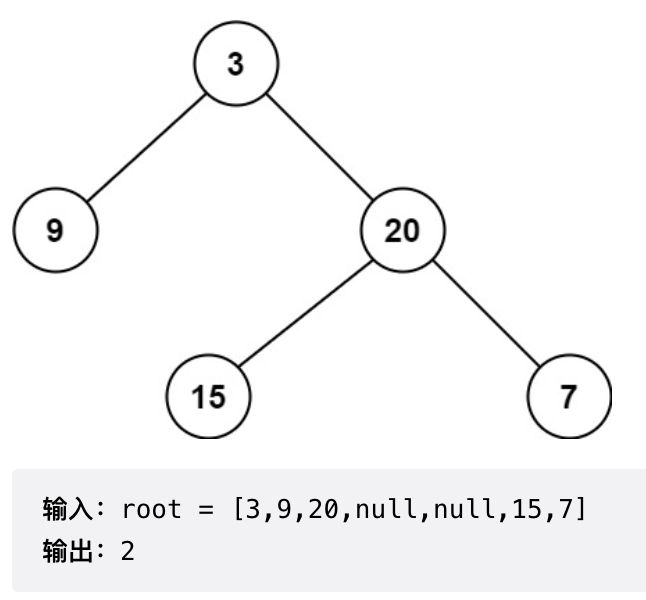
解析
1)假设已经知道左子树和右子树的最小深度,那么整体的最小深度就是左右较小的值+1;
2)所以这又是一个分治思想问题,递归处理即可;
3)递归终止条件,就是当前节点左右子树都为空。
代码示例
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if not root.left and not root.right:
return 1
min_depth = float('inf')
if root.left:
min_depth = min(self.minDepth(root.left), min_depth)
if root.right:
min_depth = min(self.minDepth(root.right), min_depth)
return min_depth + 1
执行用时:520 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 36.84% 的用户.
本文为 陈华 原创,欢迎转载,但请注明出处:http://ichenhua.cn/read/375



